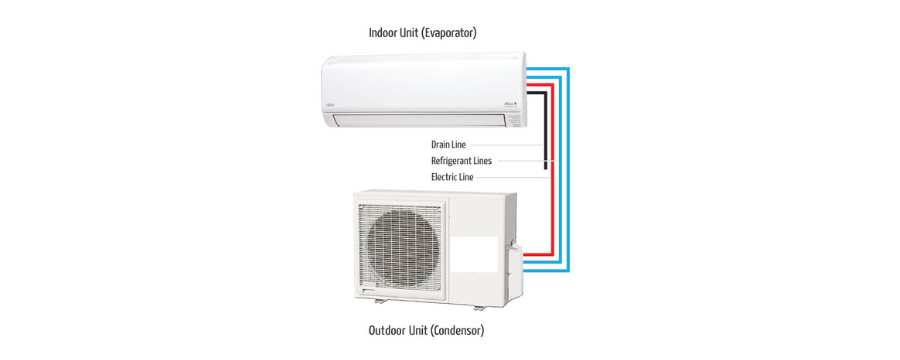
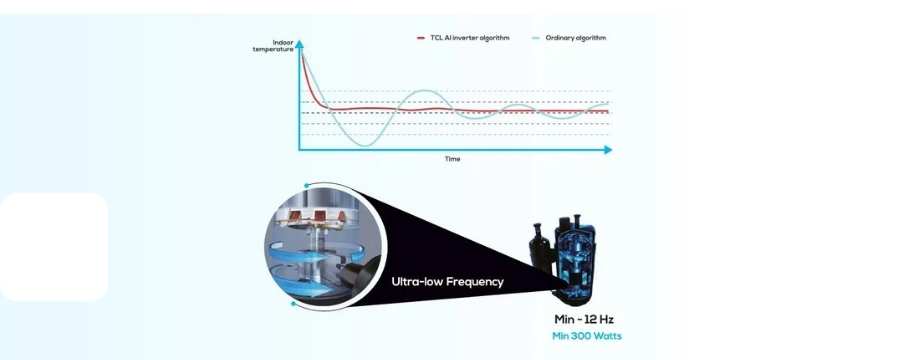
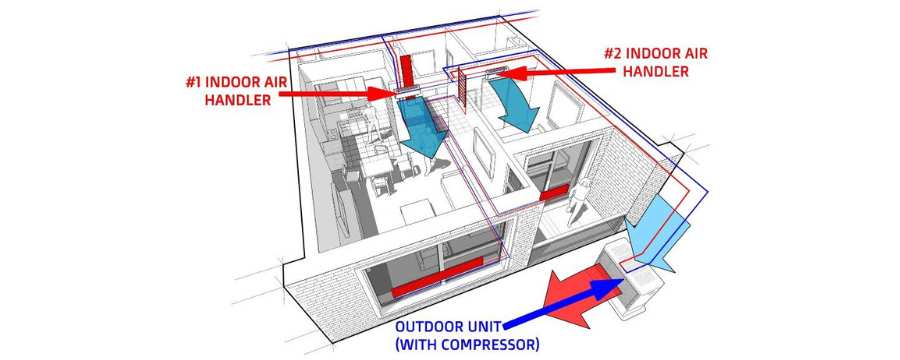
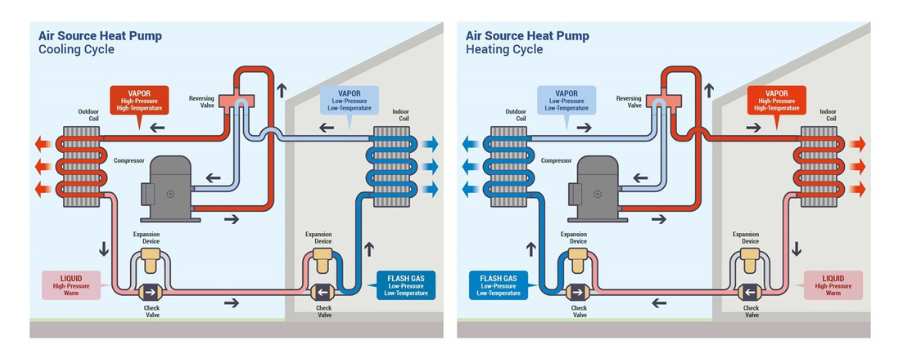
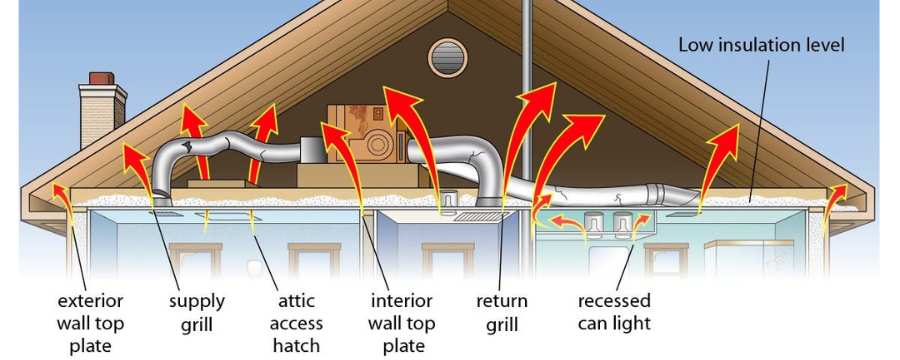
As winter approaches, maintaining a warm and comfortable home becomes a top priority. Unfortunately, even the most reliable heating systems can experience problems, often at the most inconvenient times. Understanding how to troubleshoot common heater issues can save you time, money, and discomfort during the coldest months of the year.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore some of the most common heater issues you may encounter, particularly during winter. Whether you’re dealing with a furnace that won’t ignite or a thermostat that’s not responding, this guide will help you identify and resolve these problems efficiently.
How to Use This Guide

This guide is organized to help you quickly identify and address common heater issues. We will begin by outlining 20 common heater issues in winter, followed by step-by-step troubleshooting tips for each problem. Each section will provide practical advice to help you resolve the issue or determine if it’s time to call a professional.
20 Common Winter Heating System Issues

Understanding the various heating problems in a house can be overwhelming, especially when you’re unsure what’s causing the issue. Below, we’ll discuss 20 common heater issues HVAC systems might face, particularly during the colder months.
1. Heating System Won’t Switch On
One of the most frustrating heater problems is when your heating system simply won’t turn on. This issue could be due to several factors, such as a power outage, a tripped circuit breaker, or a malfunctioning thermostat. Start by checking if your system is receiving power. If everything seems fine, your thermostat may need to be reset or replaced.
2. Furnace Does Not Ignite
If your furnace isn’t igniting, your home will remain cold despite the system being on. This can be due to a faulty ignition switch, a dirty burner, or a problem with the gas supply. If you suspect the issue lies with the gas supply, it’s best to contact a professional to avoid potential hazards.
3. Low or No Airflow from Vents
Troubleshooting central heating often involves dealing with low or no airflow from vents. This issue can result from blocked vents, a dirty air filter, or problems with the blower motor. Check for blockages first, and if the problem persists, it may be necessary to clean or replace the air filter.
4. Adjusting Your Thermostat Doesn’t Do Anything
When adjusting your thermostat does not affect the temperature, it could be a sign of a malfunctioning thermostat or wiring issues. Start by ensuring that the thermostat is set correctly and has working batteries. If the problem continues, you might need to replace the thermostat or check the wiring.
5. Cool Air Blows from Vents When the Furnace Operates
One of the reasons for central heating not working effectively is when cool air blows from the vents. This can happen if the furnace isn’t heating properly, which might be due to an issue with the pilot light, gas supply, or heat exchanger. You may need to inspect these components or call a professional for a more in-depth analysis.
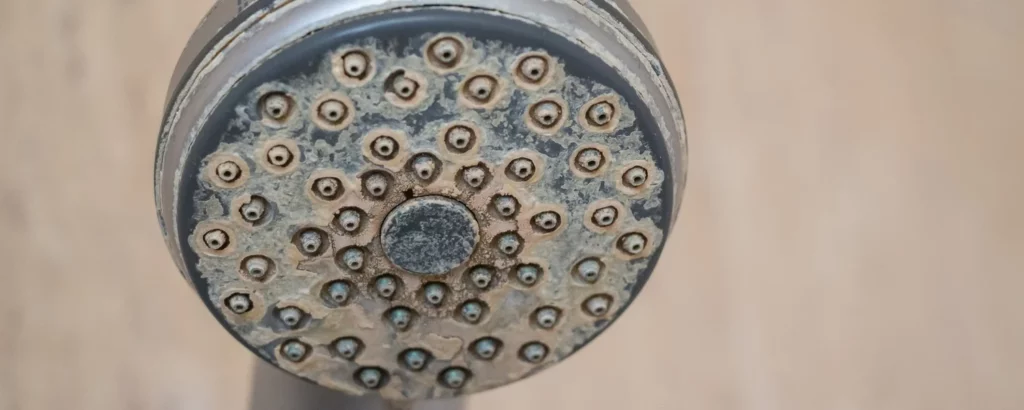
6. Air Filter Clogs Quickly
A rapidly clogging air filter can lead to several heating problems in a house, including reduced airflow and efficiency. If you find that your air filter needs frequent replacing, it could be due to excessive dust or debris in your home, or it may indicate a more serious issue with the furnace or ductwork.
7. Thermostat Not Turning on or Appears Blank
A blank thermostat screen can be alarming, especially when you’re dealing with common heater issues. This problem could stem from dead batteries, a tripped circuit breaker, or a blown fuse. Try replacing the batteries first. If that doesn’t work, check your electrical panel to ensure the thermostat is receiving power.
8. Furnace Creating a Burning Smell
A burning smell coming from your furnace can indicate several heater problems, such as a dirty air filter, dust on the heat exchanger, or even electrical issues. If the smell persists after changing the filter, it’s crucial to have your furnace inspected by a professional to prevent any potential fire hazards.
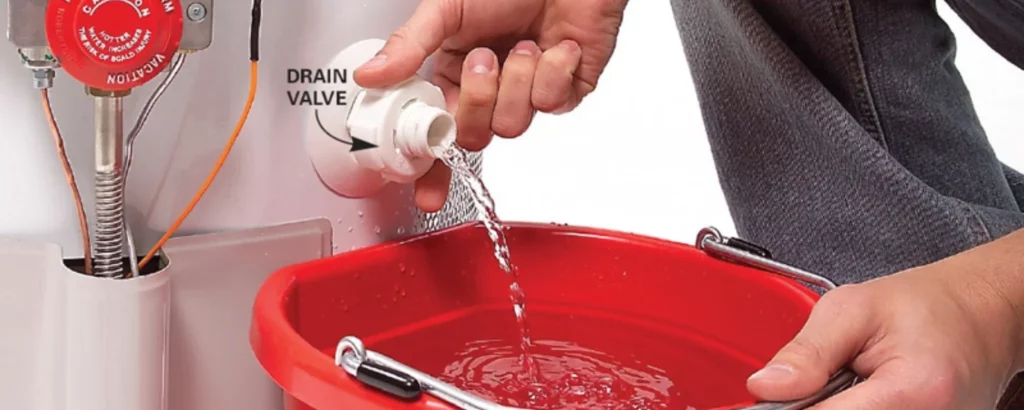
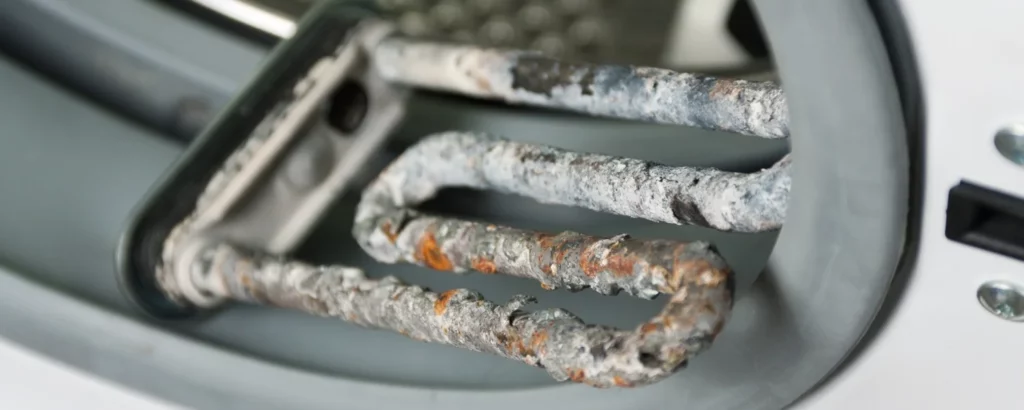
9. Water Pooling Around Heating Equipment
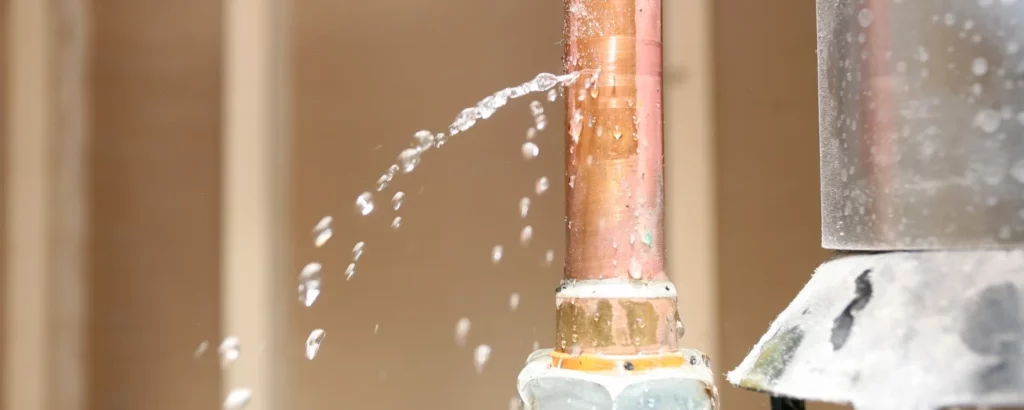
Water pooling around your heating system is a sign that something is wrong. This could be due to a clogged condensate line, a malfunctioning humidifier, a leak in the heat exchanger, or a need for water heater repair. Since water damage can lead to further complications, it’s essential to address this issue as soon as possible.
10. Heat Pump Not Warming Your Home
Heat pumps are efficient, but they can sometimes fail to warm your home adequately. This problem might be due to low refrigerant levels, a frozen outdoor unit, or a malfunctioning compressor. Checking the outdoor unit for ice buildup and ensuring proper airflow can help resolve this issue.
11. Your Home Has Lots of Cold Spots
Experiencing cold spots in your home is one of the common heater issues in a house. This issue can arise from poor insulation, blocked vents, or an improperly sized heating system. Ensuring that all vents are open and unblocked and that your insulation is up to standard can help eliminate cold spots.
12. Heating System Short Cycles
When your heating system turns on and off frequently, it’s known as short cycling. This can be caused by an overheating furnace, a malfunctioning thermostat, or a blocked air filter. Short cycling not only makes your home less comfortable but can also lead to increased wear and tear on your system.
13. Furnace or Air Handler Interior Visibly Dirty
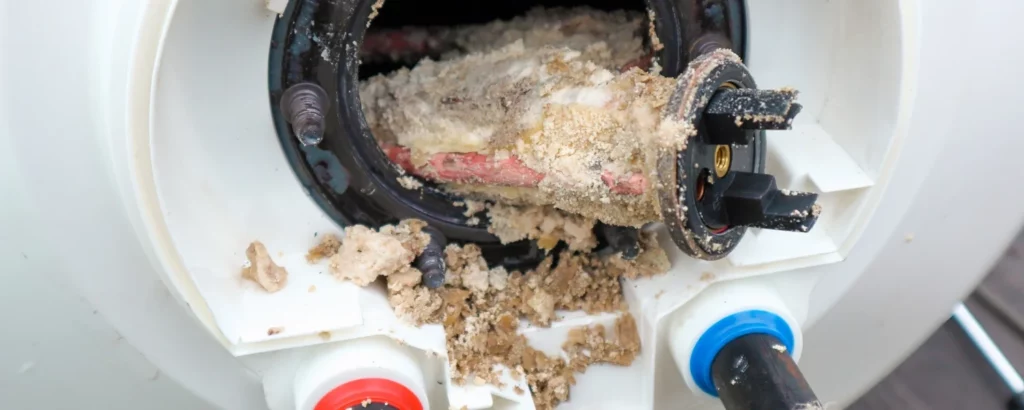
A dirty furnace or air handler interior can reduce efficiency and lead to various common heater issues HVAC systems experience. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the components and replacing the air filter, can help keep your system running smoothly.
14. Excess Humidity in Your Home
Excess humidity can cause discomfort and contribute to heating problems in a house. If your home feels damp or the windows are frequently foggy, your heating system might not be removing enough moisture from the air. This could be due to a malfunctioning humidifier or poor ventilation.
15. Your Heating Bills Are High
A sudden spike in your heating bills is often a sign of common heater issues. This could be due to a dirty air filter, a malfunctioning thermostat, or poor insulation. Identifying and addressing the root cause can help you reduce energy consumption and save money.
16. Carbon Monoxide Detectors Sound Frequently
If your carbon monoxide detectors are sounding frequently, it’s a serious issue that needs immediate attention. Carbon monoxide is a dangerous gas that can be produced by a malfunctioning furnace or blocked chimney. If you suspect a carbon monoxide leak, evacuate your home and contact emergency services immediately. For your safety, it’s essential to schedule furnace repair and service to ensure your system is functioning properly and to prevent future issues.
17. Noisy Heating System
Unusual noises coming from your heating system, such as banging, rattling, or squealing, can indicate various heater problems. These noises may be caused by loose components, a failing blower motor, or debris in the ductwork. It’s essential to address these noises promptly to prevent further damage.
18. Furnace Needs More Repairs Than Normal
If you find yourself calling for repairs more often than usual, it may be a sign that your furnace is nearing the end of its lifespan. Frequent repairs can become costly, and it may be more economical to invest in a new heating system.
19. Furnace Stays On
A furnace that stays on continuously can lead to overheating and increased energy costs. This problem might be due to a malfunctioning thermostat, a stuck relay, or a blocked air filter. Resolving this issue quickly is important to avoid further damage to your system.
20. Thermostat Displays a Service Message
Some modern thermostats will display a service message when there’s an issue with your heating system. This message could indicate various problems, from a dirty air filter to more serious mechanical issues. It’s crucial to address any service messages promptly to ensure your heating system continues to function properly.
Conclusion
Dealing with common heater issues, including tankless water heater service, can be challenging, especially during the winter months when your heating system is most needed. However, understanding these common heater issues in winter and knowing how to troubleshoot them can help you maintain a warm and comfortable home. By addressing heating problems in a house as soon as they arise, you can prevent minor issues from becoming major, costly repairs.
Remember, while this guide provides comprehensive troubleshooting tips, some problems may require professional assistance. If you’re ever in doubt or dealing with a serious issue like a carbon monoxide leak, don’t hesitate to contact a qualified HVAC technician. Your safety and comfort are paramount, and taking prompt action can ensure your heating system operates efficiently throughout the winter.
Life Mechanical offers expert solutions for common heater issues, ensuring your heating system operates efficiently during winter. From diagnosing problems like low airflow or thermostat malfunctions to providing timely repairs and maintenance, their skilled technicians help you stay warm and comfortable, preventing costly breakdowns and enhancing your system’s performance.